Break in the Clowds#
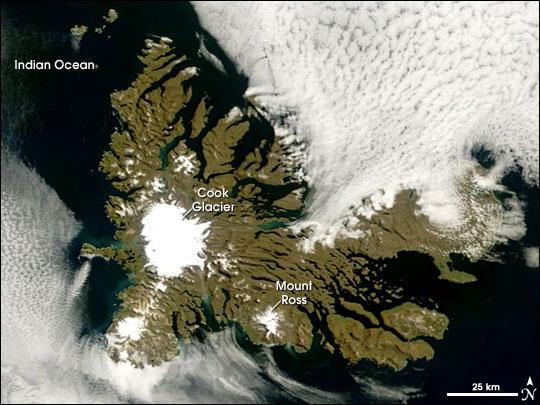
At a latitude of about 49 degrees south, the islands lie in the path of the "Furious Fifties," a belt of westerly winds that whip around the Southern Hemisphere, mostly unimpeded by land. The islands were formed over millions of years by a series of lava flows.
The perimeter of the large island is carved by fjords, and the rocky landscape is very sparsely vegetated with grasses, mosses, and a plant in the cabbage family. Glaciers are scattered across the island. The largest is Cook Glacier, in the west. The highest point on the island is Mount Ross, which has an elevation of 1,850 m; it is also thought to be the youngest volcanic peak on the island. In a handful of fjords, the water appears greenish.
The color is probably due to very fine sediment ground down by the enormous friction the glaciers generate as they scrape over the land. Rivers and streams flush this sediment out to the coast. Despite the challenging climate, several animals and birds make their homes at Kerguelen or use it as a stopping over point in their migrations or during breeding.
Among the wildlife on the Kerguelen Islands are several species of penguins, elephant and fur seals, and dozens of species of birds, including terns and albatrosses. The sea makes this "wildlife sanctuary" possible; the islands are located along the Antarctic Convergence Zone, where the icy waters of the Southern Ocean meet the warmer waters of the Indian Ocean.
The waters in this mixing area are very rich in nutrients, which support ocean plants (phytoplankton) that are the foundation of the ocean food web.