Float Walker - New Mobility in Cities#
von J. Günther und P. Kotauczek
Summary#
People were always mobile and will remain so. New alternatives must be offered. The name “automobile” cannot be used any more. Both parts of the word are no longer justified. It is not "auto", not independent and automatic, it must be controlled. And it is in its mobility restricted, reduced, by laws and regulations.
A new type of vehicle is coming that is neither a bike nor a car. In average 1,2 people travel with a car. New vehicles should be designed for a maxiu of two persons.
“Individual mobility" has a big future. As our society and the infrastructure has fewer pedestrians a new way of "walking" is expected: 'Electrical Walking", a supported and accelerated of walking. The “Float Walker” is such a vehicle. It is an electrically powered vehicle. The energy is obtained from electric batteries. They will probably not be reloaded, but supplie with spare batteries - so-called “energy-bottles”.
Environmental and social conditions#
Immobility#
The traffic of the 21st Century suffers from the disease "immobility". On average an Austrian motorists spends 78 hours per year in a traffic jam. This is called "Floating Parking". The individuality of driving got lost.
Despite increasing obstacles while driving and increasingly rising costs individual car traffic is still growing. Today's driver is in city traffic a self-promoter. The drivers of cars have less and less authority over their vehicles: more assistance while driving makes them less and less important. Parking sensors, automatic braking distance, cruise control and much more take away self-involvement. It started with the first traffic light that began to restrict the freedom.
„Headrests View Generation“#
The psychology of the motorist has no regard for facts and rational cost calculations. A change can be expected from the first generation of drivers who grew up "with the view of the headrest." So those children who strapped in a car seat while driving could see only the back of the front seat. They have a different approach to driving. They have not experienced the passing of the car windows freedom of the countryside. For them it was a transport from A to B without any adventures on the way. For them, the "drive" has become irrelevant. For them, the transport function in urban areas with their cost-benefit ratio is not of interest. The average speed in the western cities is 16 to 24 kilometers per hour. In the German city of Cologne, the average speed is only 20 kilometers per hour, but in many other European cities already 10. The transport speed of a car has reached the speed of a bicycle or a pedestrian.
New Values#
Driving today needs other values. Prestige and power of the engine need to be replaced by other items. Terms such as
- economical,
- environmentally friendly and
- easy.
Individual Mobility#
If every point should be reachable from any point, then this is to a large extent only individually possible.
Thus, "individual mobility" has a big future. As our society and the infrastructure has fewer pedestrians, a new way of "walking" can e expected, like 'Electrical Walking ", a supported and slightly accelerated walking.
Like an electric toothbrush accelerates tooth brushing and increases the quality, an electronic pedestrian is a new way of transportation adapted to the new environmental conditions.
Cities#
In the 19th and 20th century cities changed basically.
The migration into the cities was the reason for this situation in 1900. People without work were forced to go to cities. Thus the population in cities increased. In Germany for example: Between 1815 and 1865 the urban population increased from 23 to 45 million, until 1910 to 65 million.
This increaset was even more significant in the Unites States. As example, Chicago had 300,000 inhabitants in 1870, 500,000 in 1880 and 1.1 million in 1890.
Changes in transport and communication technologies were the changes at the beginning of the 20th century. New infrastructures emerged and so life was different. The functions of housing and streets were new defined. Today we need the same process. Cities are no longer defined by boarders, they are defined by functions. In the Middle Age the only possibility for people to get in contact was personally. Transport was the important factor. Old cities with broad streets and places were constructed for personal communication. Infrastructure of telecommunication is changing this situation.
Today, this ancient idea – reflected in the Oxford definition of a community as a “body of people living in one place, district, or country” – is eroding; a community may now find place in cyberspace. The new sort of site is not some suitable patch of earth but a computer to which members may connect from where ever they happen to be. The foundation ritual is not one of marking boundaries and making obeisance to the gods, but of allocating disk space and going online. And the new urban design task is not one of configuring buildings, streets, and public spaces to meet the needs and aspirations of the civitas, but one of writing computer code and deploying software objects to create virtual places and electronic interconnections between them. Within this places, social contacts will be made, economic transactions will be carried out, cultural life will unfold, surveillance will be enacted, and power will be exerted.
The future city?#
Skyscrapers, satellite cities; Vertical expansion – elevator – versus horizontal expansion by car or public transportation facilities?
One point is secure: Cities of the 21st century will not have a center, infrastructure will be equal. Inhabitants and their needs can be distributed equally because of telecommunications. European cities like Paris and Vienna can hardly be new designed. But new cities will have a new outlook. In South China – in the North of Hongkong – 10 cities have a common network. At the beginning of the 21st century they had 16 million of inhabitants. In 2020 they predict a number of 36 million. Such “big cities” will emerge because of networking. One example is the Chinese city of Wuhan, which was formed out of the former cities of Wuchang, Hankou and Hanyang. The new city name "Wuhan" is made up of letters of the previous three cities.
| city | population |
|---|---|
| Mexico City | 18.8 |
| Sao Paolo | 20.8 |
| Lagos | 24.2 |
| Karacho | 18.7 |
| Bombay | 27.7 |
| Beijing | 18.7 |
| Shanghai | 23.8 |
| Tokio | 28.8 |
| Djakarta | 28.8 |
population in 2015; figures in million
To compare the above mentioned figures - the cities at the beginning of the 20th century:
| city | population |
|---|---|
| Chicago | 4.2 |
| New York | 1.4 |
| Paris | 3.3 |
| Berlin | 2.4 |
| St. Petersburg | 1.4 |
| Vienna | 1.9 |
| Tokio | 1.5 |
population in 1900; figures in million
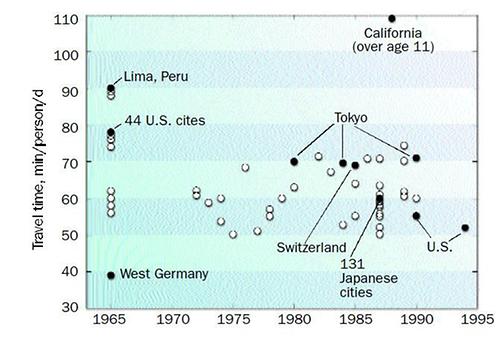
Cesare Marchetti found a relation between maximum size of a city and the respective transportation possibility. The inhabitant of a city wants to reach every place from the center on within one hour. In the Middle Age the distance was 3 kilometers, today by car 80 kilometers.
The Viennese traffic planner Prof. Hermann Knoflacher[1] has the same opinion. According to him people have to three ways per day in average, which takes 70 to 80 minutes.
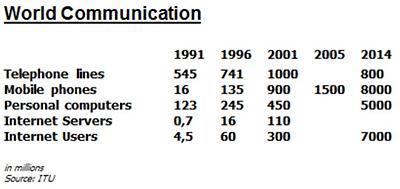
But also the houses in the cities are underlying changes. “Smart Homes” are homes with internal infrastructure. Data exchange with service providers is rapidly growing. More and more households have a network:
Home#
The increasing mobility needs a new definition for the own residence. Leader of a family are investing a lot of money to build up their own house. When parents die, children are the new owners.
The relation to the place of birth is decreasing. Place of birth and place of dying are different in many cases. The art of living is changing. Families are smaller and single households are on their way forward. The planners of flats have to consider this trend. Single households are often without anybody. They need more technical equipment like automatic care for flowers and automatic coffee machines.
People are always leaving their home places to settle down in a new country. Between 1800 and 1914 50 million people were leaving Europe and started a new life in America. In the 20th century the movement was noted toward North America and from Europe to Latin America. In 1984 the United States registered half a million immigrants. Cities like New York, Los Angeles and San Francisco have 25% of foreigners.
Also in Europe the situation is new one. France has 3 million of “black people”. The number of residents in Austria rised by 1 million due to the political turn in Eastern Europe. Wars are responsible for immigrants. In the year 2000 21 million of people worldwide left their home countries due to war. In Europe 7.5 million were victims because of the war in Yugoslavia.
One fact of making people homeless is to forbid the mother language. New leader often introduce a new official language which is not the same as the mother language.
Some million people are changing their home places in one year. They settle down in a new country and bring along their cultures and religions. Culture is a part of communication. Besides the language, different point of views and experience are forming the human identity.
In past times moving groups have not always respected the culture of the host country. Densely populated regions with better economic preconditions are prefered for new homes. How many people can planet earth accommodate?
The population explosion is going on:
- 12,000 years ago the population of the world was 5 to 10 million people
- During the 17th century population started to grow rapidly
- In 1804 world´s population was 1 billion
- In 1927 2 billion; the reason was the industrial revolution and the increased agriculture
- 1960 3 billion
- 1974 4 billion
- 1987 5 billion
- UNO is estimating 8.9 billion until 2050
The new virtual groups will not replace the traditional home. The ethic and the nation are not disappearing as predicted. If you don’t accept the new medias and communication tools you will fail in continental, transcontinental and transcultural communication. You are not able to cope with global networks and its local presence. This situation threatens parts of the world which are worse off because of educational, infrastructural, economical and political preconditions. But thus leading not automatically to a development at the cost of non- industrialized countries. The changes in the Asiatic and pacific regions showed us this. Processes like in Europe show that changes can heavy influence the traditional industrial regions.
Globalization makes is more difficult to distinguish between the states. Languages can used as borders but minorities in neighbor states are arising.
Culture is one of a kind. But internationalization is reducing the difference between several cultures. John Stratton says: “Nation – states seek to homogeneous and define themselves as different from other nation – states.”[2]
Electric Mobility#
"Electric mobility is the use of electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles with all-electric drive option (full hybrid) for the performance of the different individual mobility needs." [3].
Electric mobility has over the traditional internal combustion engine ecological and economic benefits. It reduces the emission of vehicles and may use different sources of energy.
The electrical engine changes the mobility behavior and creates new means of transport. From electric scooters on the eBike to the “Float Walker”.
Today we speak of the "body electric." The human body is supported by electrical drive. Whether this is an eBike, a “Float Walker” or eBaby-Buggy.
The traditional car industry has failed so far. "It has done a lot and there is nothing happening," said the expert Tumminelli.[4] Although this industry looks back on the longest experience. Already in the 19th Century, electric cars were offered. Grand Duke Michael of Russia went in exile in Paris with an electric locomotive, which he strained in city driving instead of the horse before the carriage. In cross-country trips he used the horses again. This was one of the first "bisexual vehicle". Today's hybrid vehicles are more a matter of satisfaction of engineers that can never be profitable.
Storage Facilities for Energy#
The effectiveness of electric vehicles depends on the battery technology. Today conventional lithium-ion batteries are inferior to the internal combustion engines of both the energy density as well as in economic terms. Because of their own weight, the batteries supply too little energy to overcome larger distances.
A conventional car needs for a distance of 500 km 37 liters of gasoline equivalent to a weight of 33 kilograms. An electric car would need a battery for the same route with the weight of 540 kilograms. In addition, the batteries are still relatively expensive.
New developments are needed.
Comparison of the energy density of important energy storage:
| Energy Carrier | Energy Density in Wh/kg | Energy Density in Wh/l |
|---|---|---|
| Mn-C (battery) | 25-70 | 120-190 |
| Alk-Mn (battery) | 80-120 | 200-300 |
| Pb (battery pack) | 20-45 | 20-100 |
| Ni-Cd (rechargeable) | 40-55 | 30-80 |
| Ni-MH (rechargeable) | 60-120 | - |
| Li-Ion (rechargeable) | 110-160 | - |
| Zinc-air Cell | 300 | - |
| H2 (liquid) | 33.300 | 2.360 |
| H2 (30 Mpa) | 33.300 | 750 |
| H2 (metal) | 580 | 3.180 |
| Methanol (liquid) | 5.600 | 4.420 |
| Gasoline (liquid) | 12.700 | 8.760 |
| Diesel (liquid) | 11.600 | 9.700 |
Refueling - Alternative Energy#

Electrical power supply is perceived by citizens as a matter of course. The frustration reactions in coverage gaps are great. These can occur time, place and functional and will make more in the future felt. First, because the current system is unstable due to increase in complexity. Second, the entitlement attitude is increasing with respect to the constant availability for the consumer. Here are clearly visible parallel to the water supply.
The water supply has several thousand years of cultural development in human history behind it and is therefore ideally suited to understand future developments in the power supply.
Both the power supply and the water supply is to ensure coverage. Here are two distribution principles have prevailed:
- Transmission system
- packaged units
Both systems have been developed in parallel and are valid for both water and electricity. Both systems coexist and are also to be found in each case where the other system is fully operational. For example, every household save in the developed industrial countries in addition to its obligatory water and power lines also a stock of containers to store well-defined amounts of water or electricity, and use mobile. That goes for bottles and cans, jars and bowls, as well as batteries for various designs. The containers have one in common: they usually cost a multiple of what is contained in them to water or electricity.
Still water and electricity is portioned in small quantities and transported in appropriate containers. The temporary stockpiling can easily be organized in this way. One can crates of beer and mineral water in the basement or dry batteries in the drawer at all times to have access to it. In developing countries with poor infrastructure that is often the only option. Production and consumption is decoupled from each other so space and time and allows a concentration of production where the conditions are best for this.
It is important to realize that a good change its legal character when is reorganized from bondage to the container line bondage. First it is a bulk cargo then. Both items have their particular legal framework. This allows electricity through lines are performed by specially authorized companies with concession, as current loads (battery commercial) is allowed with the normal trading business license. The packaging defines the legal status.
The wired telephony had their power supply from the mains. The mobile handset uses the energy in the "container", with battery. The phone has only achieved through this mobility and the strong breakthrough to widespread use.
The current thrust of the power company, it was for electric cars and ebikes "pumps" in which power can be loaded set up. This is a pioneering status and you can still indicate no effective infrastructure. Even if the pump is reached, the charging time will still unacceptably long.
The “Float Walker” pursues a new concept: replacing batteries
Networked Mobility#
Any form of transport praises its options. The bus of the dense network in the city; the train, the high speed; car sharing the loss of their investment; eBikes the vigor saving driving; etc Each transport system has its advantages and disadvantages, which looked at in a whole could bring benefits to the consumer. Networked Mobility allows the traveler to use all forms of transportation, from bicycles to taxi and to the aircraft. A colleague came with his “Float Walker” to a seminar. From there he went to the nearest available car sharing car. This car took him to the city boundary, where his own car was waiting for the cross-country trip.
A network must coordinate the different forms of transportation. If the local bus departs 2 minutes before the arriving train, he has missed his functionality.
Flexibility could give back individuality.
Future Vehicle of the City#
Increasingly, the car is expelled by politics from the city. Paid Parking, reduction of parking space and low transport speed spoil the use of the traditional "automobile". Extreme political parties are also intended to prohibit private urban mobility. People were always mobile and will remain so. New alternatives must be offered. We cannot use the word "automobile" any more. Both parts of the word are no longer justified. It is not "auto", not independently and automatically, it must be controlled and it is in its mobility - "mobile" - restricted, reduced. A new type of vehicle is coming, who is neither a bike nor a car. In average 1,2 people travel with a car. New vehicles should be designed for maximal two persons.
The transition to a new generation takes according to experts about 30 years[5]. All alternatives offered today are pioneers and temporary solutions to a new type of vehicle.
Lacunarity#

Each complex traffic system has gaps. This also applies to systems of passenger traffic. The gaps are created wherever the person to be transported boarding a vehicle leaves or puts the subsystem. If a trip begins, the person must reach – from the own position A - the position B where the vehicle stands. At each change of system the way of transfer must be done: from the taxi to the train or the train in an aircraft. This transfer must be done by own funds. Usually he is relying on the natural resources of his body, not only to themselves but also to transport some luggage. This phenomenon of gaps is called by Mandelbrot “Lacunarity”. "A fractal is called lacunar if it has large gaps, that is, if the gaps include large intervals.”[6] Lacunarity of a mixed traffic system is a measure of the loss of convenience of the traveler.
The most popular case is currently the own parked car right outside the front door. The car can be parked everywhere on a reserved parking space in front of each goal (work, shopping, entertainment destination). This ideal has led to the known problems of space requirements and various displacement phenomena. Since this ideal is associated with very high expenditure on infrastructure and is already abuts hard physical limitations, some lacunarity in the transport system is inevitable and growing. In the minds of road users “Lacunarity Liberty” is enshrined as a desired destination. Nobody wants to go far in his pickup spot, no one wants to travel long distances between transport systems on foot. Even those people who want to enjoy walking the pickup spot in front of the house and are the exit point immediately have arrived. Each lacunarity in the system is therefore perceived as a deficiency.
Complex networked traffic systems are generating inevitably lacunarities. This regularity can be observed everywhere where technically different systems meet each other. Typical examples are large railway stations, airports or ports. For such bodies come together various transport systems and are in the toughest competition interface. The planner must therefore always make priority sequences, which in turn act increasing lacunarity. Nowhere have to cover such a wide walkways in large modern airports or shopping malls. If one has the misfortune to have to use a less privileged transportation for arrival, you can very quickly accumulate a few kilometers for transfer. Anyone who has ever experienced a flight connection with overnight in London Heathrow knows what should be expressed here.
The larger the cities, and the more people there live in a confined space, the more oppressive problems of lacunarity. The road users have not only an objective time and effort but also a significant problem frustration potential. Overcome the constraint of time and distance gaps fit and conform to the system to have, is perceived more and more as a restriction of freedom and life of theft. It leads to stress and unpleasant feelings. Although the experts know these relationships, they cannot stop with the current concepts the growing lacunarity.
Aging#
We live in a time in which overaged our society. Statistically, people are living longer and stay longer healthy and active.
The World Health Organization WHO defined people aged 65 years as "old". In the gerantological research, old people are grouped into:
- "Young old" (60-75 years),
- "Old old" (75-90 years) and
- "Ancient of Days" (90 + years).
The "young old" are still healthy and fit, while the "old old" have age-related limitations and health problems. The population structure of all developed countries towards developing into a "superannuated society." As an example, Austria stated:
| Year | below 20 | 20-65 years | more than 65 years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 20 | 62 | 18 |
| 2014 | 20 | 62 | 18 |
| 2015 | 19 | 62 | 19 |
| 2020 | 19 | 61 | 20 |
| 2025 | 19 | 59 | 22 |
| 2030 | 19 | 57 | 24 |
| 2035 | 19 | 55 | 26 |
| 2040 | 19 | 54 | 27 |
Structure of Society of Austria
2013 – 2040
Source: Statistik Austria 2012
Figures in percent
This statistic shows, that the percentage of young people is stable. Middle age society is shrinking and the percentage of old people is growing.
Austrias working level is shrinking and retiered persons are more and more.
Such older people are, such less more they have to manage all activities like shopping etc by walking.
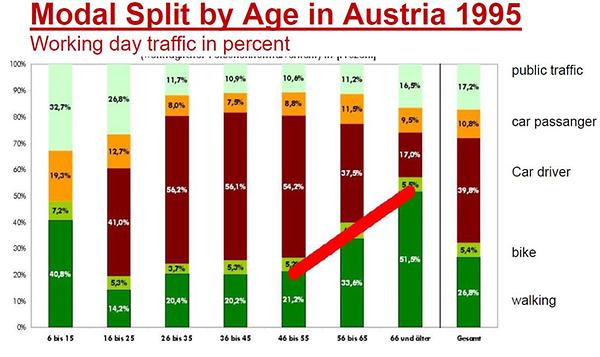
Lacunity has higher priority in higher ages. The percentage of walking people is higher in the range of 46 years and older. Older people are less mobile and they have more need for “electronic walking”.
This is also reflected in a statistic with a modal split by age:[7]
Float Walker#

The “Float Walker” is based on this. It would be a success, when the transfer-transportation can be switched over to a positive experience. If it is possible also minimize the gap between the different transportation systems, there would be more flexibility. Currently every user of transport systems tries to keep the number and size of the missing links as small as possible. It takes extra effort to track and time to themselves in order to have less change or relocate the system change to a place that is psychologically appealing. The planners of the shopping centers have recognized and are aiming for locations where as many transport systems form a hub. An existing gap is for leisure time activities. But not on every hub a shopping center will be build. In addition, each shop in turn holds an individual transport problem in itself. The consumer must carry the bought goods. Not at every hub an appropriate infrastructure can be build. Passenger of public systems must bring their own infrastructure component. Like their smartphone. "Bring your own device" is a buzzword in the networked communication system.
In peripheral areas, where transport systems are already wide-meshed, the interface resolution is often even more dramatic. What is therefore needed is a "glue" that fills the gaps.
This "glue" could be the “Float Walker”. It is to small electric vehicles, which can meet a number of conditions in order to qualify as a walking float devices. Which criteria? The “Institute for Human Computer Science”[8] has defined 18 criteria:
Weight#
The weight of a “Float Walker” is crucial for its energy balance and handling. The IHI[9] postulated that a “Float Walker” should be much lighter than the last, which will be carried. This means: one person with 80 kg and a shopping gross load (+ shopping bag or box) of 30 kg. The gross weight of a loaded “Float Walker” is therefore more than an average adult person can carry at least one kilometer without a break.
The factor between payload and vehicle weight should be much smaller than 1. In the previously tested marketable devices factors were measured under 0.2.
Cover Volume#
The bounding volume is the space that the equipment in running order measured by the maximum points occupies. It is derived from the maximum width times the greatest length times the maximum height of the device in running order without driver and load.
An electrical car like a SMART corresponds to a reference size about 1.7 times 2.5 times 1.45 = 6.16 m3. A ride with a “Float Walker” should need a cubic meter of space consumption, which is one sixth of a small e-car. The bounding volume is taken for the consumption of surface transport.
Hopp-on/off-Characteristics#
The Hopp-on/off-Characteristics of a vehicle expresses the speed and simplicity to mount the device in order to start driving. While descending all the arrangements and movements are included in the assessment, which secures the device in place standing so against accidents or falling over, to park it unattended.
This property is extremely important for shopping- or stroll rides, as it ensures comfort during frequent stops. Even for older or handicapped people is the Hopp-on/off often very stressful. For example: high stairs of public transport with automatic doors can be extremely exhausting; especially for people who need to carry a heavy shopping bag,. Even the get out in a small car can be very stressful for seniors.
Electroless Characteristics#
The electroless characteristic is the most essential factor for safety. Since in an e-vehicle ever a power failure may occur due to short circuit, battery weak or contact failure without warning, it is very important how the car behaves then.
Will it fall over? Maintain the braking ability? You can easily push it as an individual? To carry away, it needs another vehicle? Do I need a special device for towing? The electroless characteristic of a “Float Walker” has to be good-natured in the sense that the unit without power stops and does not fall. Even the recovery from danger zones must be possible for the driver alone and without help.
Incline Test#
All vehicles had to cope with a similar ramp. It was measured, how far the vehicle has been suspended for walking on the ramp and how much help the driver had to give.
Every trip line on the ramp was allows - also serpentine driving. Assessed was the height attained. Dismount and push was prohibited. At the same height gain on the ramp counts for the time spent.
Off-Road#
On a defined test track (forest) it was determined how fast and comfortable the route is manageable for a driver. At the same time, the shock poverty decides (as an indirect suspension feature) on the head and wrists of the driver. Wheel diameter and tire section are the dominant factors.
Balance#
Compared, is how quickly a person can hold the device without fear and roadworthy in balance. Another criterion is how the driver can respond to natural tendencies of the vehicle in an eight loop test and whether special training is required.
Price#
In the comparison test the cross purchase price (delivered free house) was used – including all incidental expenses.
Operating Distance#
The range is a very insecure comparison criterion, especially when the vehicles are close together in their performance. Depending on road conditions, wheel size, wind and temperature change various distances are measured. The drivers help also can be very different and affect the range much.
To minimize this methodological uncertainty all vehicles are tested by the same driver (same physiological efficiency) and ranked. Waived must be measured on an absolute route, so only the relative distance scale comes in the evaluation.
Beer Box Test#

This test is based on the assumption that a recreational transportation funds should also be used to bring a box of mineral water or beer from a local shop for a garden party. It will be measured, how much the driver needs to transport this one kilometer wide. The load attachment, the simplicity of the store and driving impairment is compared. Only a few vehicles, meet this criterion.
Patch Test, Parking in a Garage#
This is compared to what extent a smaller number of 4 vehicles (equivalent to a family with two children) can be parked ín a detached garage. Whichever is the floor space consumed and whether the vehicles nested (such as stacking chairs) could be. The units must be parked in a form, that they can be used (not folded).
Foldaway#
There will be compared, how simple a device can be reduced by folding in its volume to stow it. Either for transportation or for parking. Also the time is taken into account, how quickly the composition laying operation can be performed by a non-trained person without aids.
Intermodality / Loading into a Car#
Compared, is how easy the device can be loaded by one person alone without help in a car.. To change the way in public transport (intermodality) is considered. Bulkiness, how it can be handled and weight are the other criteria for comparison.
Turn Radius#
There will be measured the smallest possible turning radius without ground contact of the feet.
Easy Use for older People#
There will be tested the acceptance by a person over 70 years. The test person will be checked in terms of well- being, joy of use and freedom from fear. See also item “Hopp-on/off”.
Individualization#
This criterion compares the opportunity to personalize the device for leisure and work so that a personal statement is made, that goes beyond the fact "I use an e-mobility vehicle". The vehicle as a fashion item and advertising to the user and its aesthetic message, such as clothing, car color, accessories, etc. (similar to the successful global strategy of the T-shirts). This criterion is intended to express the psychological acceptance (fashion capability, fun factor).
Refueling#
This measures how long the unit will be shut down as a minimum in order to "refuel" reassessed. Backup battery systems have a clear advantage.
According to these criteria a ranking of existing products can be made. Existing benchmarks are published on the Internet.[10] Of course, other and more stringent criteria are applied.
In addition to the technical requirements, the “Float Walker” concept also includes another change in behavior of users and the system operator. It must be demonstrated by appropriate testimonial personalities of public life, that the use of such electric micro-devices can achieve more quality of life. This fact had surprised the author Prof. Kotauczek in his self-test positive.
Changes are possible, when lightweight design and good design devices will come to the market. This can meet the above criteria perfectly. It also needs a critical mass of first mover. Then the responsible authorities must decide whether they accept the “Float Walker” as a separate group of road users or include them in an existing category. This is a sociological process, which still holds many areas of conflict. Just think of the issue of portability in the various existing public transport systems, the equalization of freedom of barrier
The previous empirical studies show that the potential has been exploited; both in psychological, behavioral and traffic in technical terms. There is still a lot of practical experience needed to achieve a transport policy for a new vehicle like the “Float Walker”. This is partly due to the very limited range of “Float Walkers” and the smallness of the active test population.
How fast can be changed?#
Cyclical changes#
People have always been mobile. In the middle age masses moved because of pilgrimages, today they are called holiday travelers.
People were never more mobile than today. Because of the increasing prosperity and the abolishment of many borders in Europe „freedom“ appears as a new symbol. Freedom leads into movement. We have to overcome the removed barbed wire borders.
Our economy needed the separation of work and therefore more mobility - of goods and managers.
Moreover, liberalized markets designed a „global village“. In the 21st century the global economy is dominated by three key industries:
- telecommunications
- computer technologies and
- tourism.
The computer section is growing 2.5 times faster than traditional fields.
The mobile economy influences also the private lives – tourism is one of the greatest economic field in the world. 11 percent of the workforce is engaged in the tourism.
Cycles have nothing in common with „fashion“. “The system of fashion with its professional and actual form represents more than a cool machinery of permanent innovation; it is an intelligent and effective mechanism against“ too much civilization”. Fashion creates a kind of puffer zone or a “time cocoon” for the mankind to protect them against the flood of information. Fashion is influenced by the society and consists of permanent coming and going; destruction results in creation. The cycles of the generations are longer and are more influencing.
Changes in technologies and generations are common developments. Old styles are replaced by new ones. New technologies are replacing old ones. Telecommunications and computer technologies have pushed us into the information society. More than 50 percent of the employees of the developed countries are working with information.
This information society brought us not only changes. The instruments helped the people to become more mobile. Mobility is nothing new for the people. The nomads can life again irrespective of the administration of a state.
Information technologies change many processes in our working environment. These changes have not only be seen technical. The background has social and economic factors. Due to new media´s traditional jobs are changing or are no longer necessary.
Starting with agriculture and industry our society is on the way to become an information society. In figures: in Germany employment in the agricultural sector decreased by 76% and in the industry by 33 % between 1960 and 1990. At the same time top-technologies increased by 44% and the high tech sector by 26%.
| top technologies | +44% |
| high tech | +26% |
| industrial production | -33% |
| agriculture | -76% |
After the world war more than 50 % of the Austrians were employed in agriculture. At the beginning of the 21st century the employment will decrease to 5%.
During the 19th century high-tech steel industries ruined small farmers. Nowadays, these steel industries become victims. Although, the number of industry employees decreased dramatically the downward trend has not already stopped. Until 2020 each fifth industry jobs will be abolished.
The service industry is the winner of this situation. Above all, the software and content production will have enormous increases. A simple camera has more software than a apple computer 10 years ago. This is effecting the costs. The software of a Minolta camera has a value of 550 euro, the lense 40 euro and the case 20 euro. Some decades ago is was the other way around with the software did not exist. Information represents a high proportion of total economy.
Hardware is the smaller part. Software is dominating the product.
The change of a board computer in a car can increase the power of the engine. The computer is managing the fuel injection more precisely and effectively. Thus reducing the need for fuel and increases the power. This motor becomes better because of an exact control. The “control part” has a higher value than the machine itself. “These new technologies represent a basic change of our society, our economy and our work.”
Although many jobs were lost – as in the agricultural sector – the job situation has improved. In 1900 the U.S. counted 27 million of workers, in 1993 125 million of them. This rapid growth is partly due to the proportion of female work.
Besides the long-term cycles changes also happens in middle-term periods.
Ups and downs in the economy are usual. The intensity of growth is sometimes slower and will be pushed by new
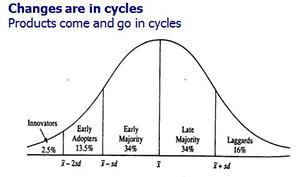
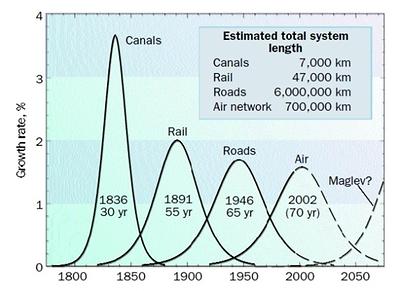
events. After stagnation and depression an upward trend follows. These cycles were often discussed. Only after research work of Cesare Marchetti[11] we know that these cycles are following a certain scheme. Old technologies are replaced by new ones. This substitution is a result of society behavior and new economic structures. They all follow certain schemes.
Marchetti started the research work with the number of fish in the Adriatic Sea. He found out that it is possible to calculate the future number of fish. Many predatory fishes reduce the number of fish and consequently the predatory fishes also decrease. The prey fishes can grow and so the cycle starts again. This result is the “S- curve” and is also used in the economy.
The cycle comprises the following steps:
- emergence (=low distribution, low growth)
- growth (=high growth, quick distribution)
- saturation
- replacement
In the meantime a lot of material for the awareness of this substitution exists:
- development of the car industry in a certain country
- increase of the world´s flight traffic and its transport volumes
- world tank fleet
- demand for primary energy of certain countries
- technological substitution of steel-producing methods
- replacement of horses by cars, etc.
Although we have the feeling that many things are developing in a quicker way, the innovation cycle is remaining constant. The innovation phase is repeating every 55 years.
The current wave can be described as follows:
- 1980: middle date between innovation and invention
- 1984: start of innovation period
- 1993: 50% of basis innovation realized and 50% of new industries founded, but with low production capacity.
- 2000: 90% of all innovation are done. Upward trend is starting.
The new developments of this cycle are:
- information processing
- genetic research
- hydrogen engines ( car and air-plan)
Within this cycle, it also comes to miniaturization. Computer and telecommunication devices became smaller. They are now often poorly operated because they were made too small.
In the production of transport is one last great revival of companions. Large cars - which have been built to be used off-road – are used in city traffic. The wave of this cycle has already peaked and will result in the downward wave of miniaturization. Cars are smaller and cheaper to operate. The "Float Walker" is a pioneer.
The discussed cycles are only middle- and long-term ones. A change above them would be called change of biosphere toward neo-sphere. Development of earth-based individuals to knowledge-based individuals. The development of a knowledge society means more spiritual and moral aspects in our behavior. A change which cannot be valued at the present time. Our lives are too short to calculate the future effects.
Weiterführendes#
Literature#
- APOSTOLATOS, Konstantinos; TAGA, Karim; SUTER, Patrik: Next Generation Networks in Europe. Broadband in 2011 and beyond, Arthur Little, 2006
- AUSUBEL, Jessy H.; MARCHETTI, Cesare: “The evolution of transport”, The Industrial physicist, American Institute of Physics, APRIL/MAY 2001
- BARTELS, Andrew: Trends 2006: Six Economic Shifts Affecting IT, FORRESTERS, 2006 BERGMANN, Frithjof: Neue Arbeit, Neue Kultur, Freiamt 2004
- GÜNTHER, Johann: „Digital Natives & Digital Immigrants“ Studienverlag Innsbruck Wien München Bozen 2007
- GÜNTHER, Johann: „Der vernetzte Egoist. Telekommunikation und Computer verändern den Menschen“, Studienverlag Innsbruck Wien München Bozen 2004
- GÜNTHER, Johann: „Die neue Mobilität der Gesellschaft“, Studienverlag Innsbruck, Wien, München, Bozen 2002
- GÜNTHER, Johann: „Verkehrstelematik“, together with Kristina ZACH, Krems 2001 GÜNTHER, Johann: “Digital Natives & Digital Immigrants”, In “Virtual University”, Proceedings 8th international Conference, Bratislava 2007, Page 11 - 22
- GÜNTHER, Johann: „The new Mobility of our Society. Caused by Telecommunications”, in: ITI 2004, Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces, Dubrovnik 2004, Croatia, Page 433-439
- KNOFLACHER, Hermann: “Virus Auto. Die Geschichte einer Zerstörung“, Vienna 2009
- KNOFLACHER, Hermann: „Stehzeuge-Fahrzeuge: Der Stau ist kein Verkehrsproblem“, Wien/Köln/Weimar 2001
- KOTAUCZEK, Peter: „Die Weltbildmaschine. Grundlagen der Humaninformatik. Von der Information zur Informiertheit”, Wien Klosterneuburg 2005
- KOTAUCZEK, Peter: “Die Kunst des Spazier-Schwebens“, Vienna 2010 KOTAUCZEK, Peter: „Beko - Das Buch“, Vienna 1998
- KOTAUCZEK, Peter: "Verkehrsplanung aus der Sicht der Humaninformatik", „BEITRAEGE ZU EINER OEKOLOGISCH UND SOZIAL VERTRAEGLICHEN VERKEHRSPLANUNG 2“, Wien 2008 https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:LPK5so0wdxQJ:www.ivv.tuwien.ac.at/fileadmin/mediapool- verkehrsplanung/News/Festseminar_Prof._Knoflacher/kotauczek- humaninformatik.pdf+&hl=de&gl=at&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESjZwxC- 3u9VjqKs41MScDYGD5XiR06gwu6Gld8a5dqSKowIweZphZBMQ2bc1WDfoLEiEfllioxP44oBrHM8svELZFs lj36pzqe7oofEjSbAFtEtkEngf43t1lKlOv-iP9bxVqr_&sig=AHIEtbRPfBEy5AMdiagAXDUAA8A4tv-DTQ
- MANDELBROT, Benoit B.: "Die fraktale Geometrie der Natur", Basel 1987 Electronic Version: http://books.google.at/books?id=bkVNilU3SvwC&pg=PA326&lpg=PA326&dq=lakunarität&source=bl &ots=KByOu1i4qO&sig=gK2J_rBhBTqrsaBDAmmqcjeL2Ng&hl=de&sa=X&ei=KCAOUbbCEMbTtQaZ5oHI Ag&ved=0CC8Q6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=lakunarität&f=false
- MARCHETTI, Cesare: “On Decarbonization: Historically and Perspectively”, IR-05-XXX, Prepared for HYDROFORUM 2000, Munich, 11-15 September 2000 * MARCHETTI, Cesare: “Productivity versus Age”, IIASA Contract No. 00-155, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, Laxenburg 2002, Austria OWEN, Martin: The myth of the digital native, http://www.futurelab.org.uk/viewpoin/art26.htm, October 2006
- TUMMINELLI, Paolo: „Ist das Auto der Zukunft noch ein Auto?“ Bank of Austria „Stadt der Zukunft“ ORF Radiokulturhaus, Vienna, 2012
- TUMMINELLI, Paolo: „New Mobility Forum 2010“, Speech: "Die Zukunft fährt elektrisch. Nur wie?", Villach 2010
- TUMMINELLI, Paolo: „Car Design America: Myths, Brands, People“, Kempen 2012 TUMMINELLI, Paolo: „Car Design Europe“, Kempen 2011
[1] Hermann Knoflacher (21.9.1940), Austrian Engineer, professor emeritus at Technical University Vienna – Institute for traffic planing
[2] John Leak Newbold Stratton (* 27. November 1817 in Mount Holly, Burlington County, New Jersey; † 17. Mai 1899) was politician in USA.
[3] http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elektromobilität
[4] Tumminelli, Paolo: „Von Tag zu Tag“, Austrian Broadcast, Radiostation OE1, October 4th, 2012
[5] Tumminelli, Paolo: „Von Tag zu Tag“, Austrian Broadcast, Radiostation OE1, October 4th, 2012
[6] MANDELBROT, Benoit B.: "Die fraktale Geometrie der Natur", Basel 1987, Page 326 Electronic Version:
http://books.google.at/books?id=bkVNilU3SvwC&pg=PA326&lpg=PA326&dq=lakunarität&source=bl
&ots=KByOu1i4qO&sig=gK2J_rBhBTqrsaBDAmmqcjeL2Ng&hl=de&sa=X&ei=KCAOUbbCEMbTtQaZ5oHI Ag&ved=0CC8Q6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=lakunarität&f=false
[7] Harry / Sommer, Bundesverkehrswegeplan 1995, by Ministry of Infrastructure
[8] http://humaninformatik.wordpress.com
[9] http://humaninformatik.wordpress.com
[10] http://bekoholding.files.wordpress.com/2012/10/4-emob-vergleichstest10x-sept-2012.pdf
[11] Cesare Marchetti (born 1927 in Lucca) an italian physician and system analyst. Experienced in the field of energy technologies and system theoretical analyses. He gave his name for „Marchetti Constant“ and „Marchetti Curve“.
' Kontrolle='Nein'}]